Difference between revisions of "MBSE Competencies"
(→Objectives) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Objectives== | ==Objectives== | ||
| − | To | + | To understand the need for guidance on application of INCOSE competencies for MBSE. |
| + | - Review the current INCOSE material on MBSE competence | ||
| − | + | - Review roles and associated competence scopes | |
| − | + | Need to understand what the output from this working group will be: | |
| − | + | - Z Guide | |
| − | + | - Omega Guide | |
| − | + | - U Guide | |
| − | + | - Paper | |
| − | + | - White paper | |
| − | ' | + | - Don't panic or other book |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==Team== | ==Team== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 23: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Andrew Pemberton | |Andrew Pemberton | ||
| − | |Thales | + | |Thales UK |
|Lead | |Lead | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 55: | Line 34: | ||
|Member | |Member | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Review of INCOSE competency framework == | ||
| + | MBSE is considered as a cross cutting technique as defined in the systems engineering handbook. | ||
| + | We need to understand what each of the competencies in the INCOSE competency framework (reference needed) means in the context of MBSE. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
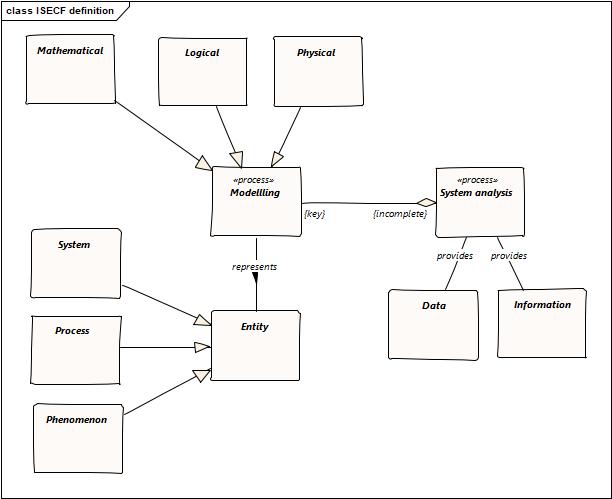
| + | Here follows a model defining the terms as used in the ISECF v1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ISECF Modelling Sys Analysis definition.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
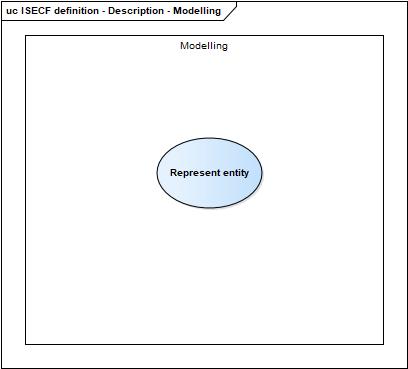
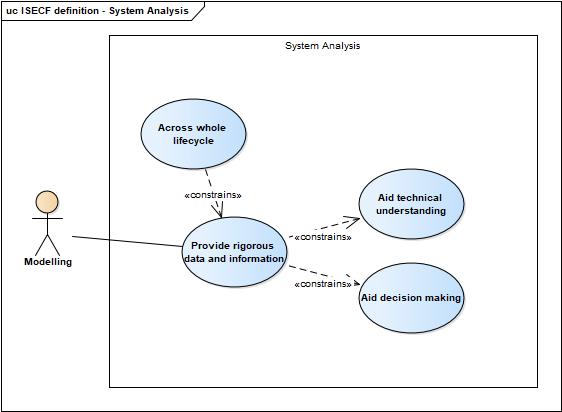
| + | And the description field also includes some ideas of why the various parts of the competency exist: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Modelling | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ISECF definition - Description - Modelling.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | System Analysis | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ISECF definition - System Analysis.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
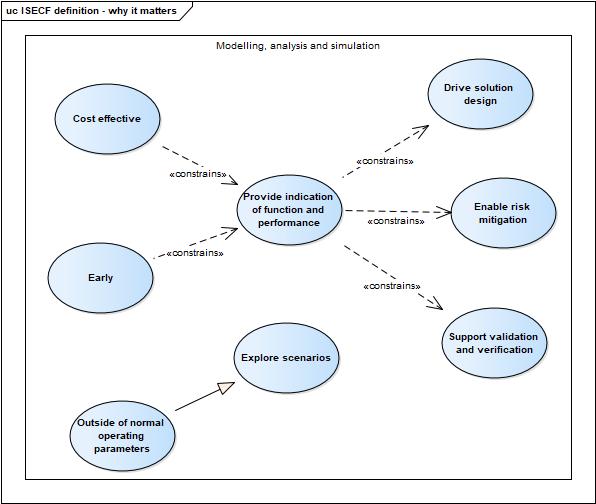
| + | And from the why it matters section | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ISECF definition - why it matters.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Next we need to look at the competency indicators, effectively what is a person required to demonstrate in order to attain a the levels. | ||
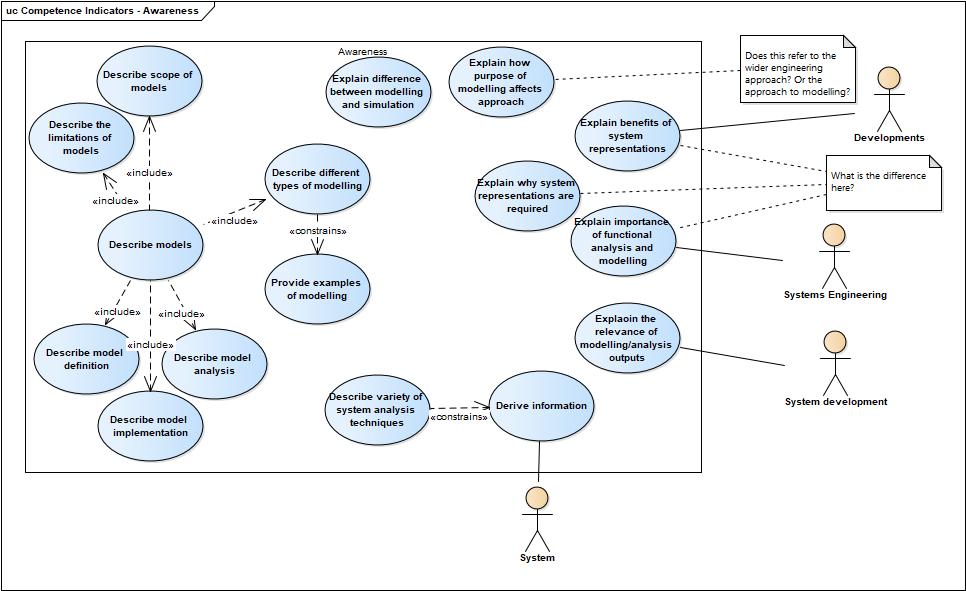
| + | Firstly Awareness. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Competence Indicators-Awareness.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The remaining levels will follow along with the linked indicators (those where they build on an earlier indicator rather than introducing something new) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Initial questions: | ||
| + | - To where does Systems analysis provide the data/information? | ||
| + | - Systems analysis appears to be almost an afterthought in this competence | ||
| + | - Systems analysis is not necessarily the only process to which modelling could be applied. | ||
| + | - How does this definition of Systems Analysis match up against he definition given in the SE handbook? | ||
| + | - the requirements from the "why it matters" section are focused on the modelling deliverables, again suggesting that system analysis is an afterthought. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Modelling Roles== | ||
==Documents== | ==Documents== | ||
| Line 64: | Line 84: | ||
!Link | !Link | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2018 |
| − | | | + | | INCOSE Systems Engineering Compentency Handbook |
| − | | | + | | INCOSE |
| − | | | + | | https://connect.incose.org/Pages/Product-Details.aspx?ProductCode=ISECFv1 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2015 | ||
| + | | INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook v4 | ||
| + | | INCOSE | ||
| + | | https://www.incose.org/products-and-publications/se-handbook | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | |||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:34, 8 March 2023
Contents |
[edit] Objectives
To understand the need for guidance on application of INCOSE competencies for MBSE.
- Review the current INCOSE material on MBSE competence
- Review roles and associated competence scopes
Need to understand what the output from this working group will be: - Z Guide - Omega Guide - U Guide - Paper - White paper - Don't panic or other book
[edit] Team
The MBSE Competencies team currently comprises the following members:
| Member | Organisation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Andrew Pemberton | Thales UK | Lead |
| TBD | TBD | Member |
| TBD | TBD | Member |
[edit] Review of INCOSE competency framework
MBSE is considered as a cross cutting technique as defined in the systems engineering handbook. We need to understand what each of the competencies in the INCOSE competency framework (reference needed) means in the context of MBSE.
Here follows a model defining the terms as used in the ISECF v1.
And the description field also includes some ideas of why the various parts of the competency exist:
Modelling
System Analysis
And from the why it matters section
Next we need to look at the competency indicators, effectively what is a person required to demonstrate in order to attain a the levels. Firstly Awareness.
The remaining levels will follow along with the linked indicators (those where they build on an earlier indicator rather than introducing something new)
Initial questions: - To where does Systems analysis provide the data/information? - Systems analysis appears to be almost an afterthought in this competence - Systems analysis is not necessarily the only process to which modelling could be applied. - How does this definition of Systems Analysis match up against he definition given in the SE handbook? - the requirements from the "why it matters" section are focused on the modelling deliverables, again suggesting that system analysis is an afterthought.
[edit] Modelling Roles
[edit] Documents
| Date | Title | Author | Link | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | INCOSE Systems Engineering Compentency Handbook | INCOSE | https://connect.incose.org/Pages/Product-Details.aspx?ProductCode=ISECFv1 | |
| 2015 | INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook v4 | INCOSE | https://www.incose.org/products-and-publications/se-handbook | - |